Although both cables look identical, Thunderbolt cables offer much more than the other type with key differences between the two types. Do you need to charge your mobile device, or connect a peripheral to a PC or Mac? You’ll probably need some kind of USB port or a Thunderbolt port.
Previously, both the interfaces had entirely different standards, leading to confusion and frustration over ports, plugs, and cables. However, in their newest iterations, choosing between the two—or just telling them apart, is confusing. Like Apple’s MacBook Pro and MacBook Air laptops have four Thunderbolt ports, but none of them carries a visible label.
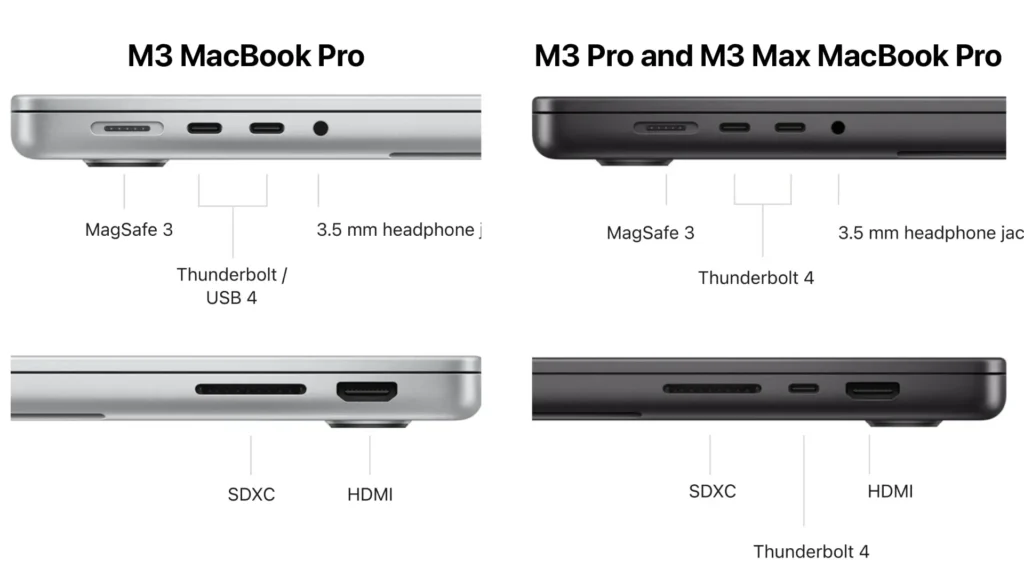
That’s because of the emergence of Thunderbolt 3,4,5 and USB Type-C (usually known as USB-C) interfaces in recent years. With the introduction of these new ports, they share identical shapes, connectors and cables, and these days device manufacturers don’t always provide label that will help you easily guess which is which.
So, to turn these assumptions into clear, visible claims, let’s walk your through the differences between Thunderbolt and USB-C, and explain which one you should use depending on which device you need to connect.
Understanding Both The Interfaces
What Is USB-C?
Universal Serial Bus is an industry-standard connector. It can transmit both power and data and looks similar to the older micro-USB connector at first glance. However, it’s more oval in shape and slightly thicker to accommodate its best feature: flippability.
However, it is important to note that USB-C does not mean any speed specification—it’s the physical shape of the connector which has become the standard across smartphones, laptops, tablets and countless other devices.
One of the main reasons for USB-C’s popularity is its versatility. This single port can engage in multiple functions, including charging devices, transferring data on varying speeds depending on the USB version, display output purposes, and reversible design.
Depending on their versions and generations, USB standards support different speeds and different purposes. USB 2.0, which was the first one, offers basic charging and low-rate data transfer with speed up to 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0, 3.1 Gen 1 and 3.2 Gen 2 provide a medium range of benefit, suitable for everyday use and fast data transfer of up to 10Gbps with USB 3.2 Gen 2.
The top-of-the-line USB-C variant USB4 offers premium performance up to 40 Gbps and backward compatibility with USB 2.0. Moreover, due to its foundation based on Thunderbolt 3, it provides compatibility with Thunderbolt devices as well.
Understanding What Thunderbolt Is
Thunderbolt is a data and display protocol developed by Intel and Apple. It uses the USB-C shape but supercharges it, becoming USB-C’s overachieving cousin. Introduced in 2011, Thunderbolt connections are meant for high-speed data transfers and enhanced interoperability between a computer and external peripherals like hard drives and monitors.
Thunderbolt 4 supports up to 40 Gbps daisy-chaining multiple devices, dual 4K and single 8K display, and up to 100W charging. On the other hand, Thunderbolt 5 doubles that bandwidth to 80 Gbps bidirectional speed (or you could say 120 Gbps in one direction with Bandwidth Boost).
It’s charging capacity is enhanced to 240W, with three 4K displays support at 144Hz or multiple 8K displays. Thunderbolt 5 also provides PCIe Gen 4 for faster external GPUs/storage, making it capable of faster and more efficient transfers.
The reason for Thunderbolt dominating the market and their rapid integration into new devices includes different factors. You can imagine the difference between the speed which a USB-C offers and that of a Thunderbolt 5, it’s double.

Thunderbolts are built for faster and efficient performance role; hence they offer better display support, offering connection of 6 devices in a chain, and it has direct access to your computer’s PCIe lanes, enabling it to boost performance.
Notably, Thunderbolt ports are backward compatible with USB-C devices as well. So, if you’ve got some peripherals that support Thunderbolt and some that support only USB-C, both should be able to work just fine with a Thunderbolt port, though the USB-C peripherals will be limited to USB-C speeds and capabilities.
Speed Comparison
Is Thunderbolt Faster Than USB-C?
Thunderbolt cables provide 2x faster speed compared to USB-C. Thunderbolt 5 offers significantly higher data transfer rates and more versatile capabilities. USB4 supports up to 40 Gbps of data transfer rate, while Thunderbolt 5 provides up to 80 Gbps of transfer rate, with an option to expand bandwidth in one direction to 120 Gbps with Bandwidth Boost technology.
However, the USB4’s 2.0 version supports up to 80 Gbps, most USB4 devices on the market still adhere to the older 40 Gbps standards. To achieve its full potential, you will need specifically labeled “80 Gbps” cables. Some USB4 cables, ports and devices support 20 Gbps, some support twice of it, and some fourfold, but all Thunderbolt 5 scenarios support 80 Gbps transfer.
That’s why Thunderbolt’s superior speed and broader compatibility is the preferred choice for professional and high-performance applications. It is ideal for content creators, gamers, and professionals who demand the highest quality visuals and performance from their setups.
Compatibility
To ensure a smooth user experience across different generations of devices, compatibility and backward compatibility matter a lot, playing a crucial role in adopting new technology.
Thunderbolt again proves itself by maintaining full compatibility with previous versions like Thunderbolt 4, 3, USB4 and USB-C devices. This backward compatibility ensures seamless use of existing technology along with the new one, making the adoption and transition smoother.
Thunderbolt 5 also supports Thunderbolt Share if you have a licensed Thunderbolt Share device. On the other hand, USB4 also provides excellent backward compatibility with Thunderbolt 3 and early USB versions. However, Thunderbolt 5 offers support to a wide range of devices and offers advanced features, making it a more comprehensive solution for future-proofing setups.
In real-world scenarios, Thunderbolt 5 significantly increases work efficiency and performance in professional workflows. It is particularly beneficial in game development where faster data transfer rates and high refresh rate display are required.

Professionals using MacBook Pro with M4 Max can connect 4 external displays which enable advanced multi-tasking and improved productivity. Thunderbolt 5’s support for external GPU and high-speed external storage enhances overall device performance, making it versatile for various applications.
Definitely, their utilization is not limited to gaming alone, they are preferred for 3D animation tasks, visual effects rendering, scientific visualization, and broadcast video editing. Although, USB4 is not advanced enough, it still offers a significant upgrade in performance and efficiency when used for same purposes as mentioned above.
Common Consumer Myths And Confusions
Can All USB Cables Do The Same Thing?
One of the most common confusions and user assumptions about USB-C is that they are the same. However, they only look similar in shape and USB-C itself only refers to the connector’s shape, not its specifications. Their internal specifications vary drastically between cables.
Do I Need Thunderbolt For Charging?
Although they are cheap, some consider them to be low in performance than Thunderbolt. The choice of any interface depends on your needs and desires. An expensive Thunderbolt cable won’t improve your smartphone charging speed.
Another misunderstanding about both is their incompatibility with each other and their predecessors. After reading this guide, you know by now that Thunderbolt ports support USB-C, though you won’t be able to utilize full potential of Thunderbolt without a proper Thunderbolt cable and device.

Which One To Choose?
Is Thunderbolt Worth Paying Extra For?
While it might seem obvious to choose Thunderbolt due to its superior capabilities rather than a USB-C, the decision isn’t always simple. In most of the cases you don’t even need to consider one over another. To see why, take the most basic capability of either port: charging a battery.
On laptops and devices which support USB-C only charging and have both Thunderbolt and USB-C connectors, there’s usually no difference between the ability of a given port to charge the system.
Another situation which may arise is the interchangeability between Thunderbolt and USB-C when you are connecting a client computer that supports Thunderbolt (say a laptop) to a device that doesn’t (like a phone or external hard drive with a USB-C cable).
In these cases, the devices will work but the laptop’s Thunderbolt cable won’t gain any performance. However, there are cases in which you might need to choose the expensive choice (Thunderbolt). This is mostly true for media professionals who frequently copy, paste, or move files and videos from device to device.
Overall, neither USB nor Thunderbolt is a clear winner. They are just different, and each excels in different use cases. Ultimately, if the history of hardware interfaces is any guide they will both be replaced by a new standard in a few years, and there will be a whole new set of differences to learn and subtleties to unravel.
Can USB-C Replace HDMI And Display Ports?
Yes, USB-C has the potential to replace HDMI and display ports due to its versatility, high bandwidth, and ability to support multiple functions through a single port. However, the current landscape still favors the use of HDMI for many consumer devices, as compatibility issues may rise.
As technology evolves and more devices opt for USB-C, it may become the dominant standard for video output in future.
How Can I Tell What My Port Supports?
You can look for a lightning bolt symbol next to the port, that will tell you that it is a Thunderbolt interface, however, you can also check this in settings.
More Guides
How Password Managers Really Work – And Are They Safe?