Password managers provide you with useful tools that make it easy to adhere to password management best practices. They are widely regarded as safe, and they provide you with a sense of satisfaction for your complex, difficult-to-remember credentials protecting your digital accounts.
Interestingly, there are more risks involved with not using a password manager. Most people use weak passwords because they cannot or don’t want to remember a bunch of different passwords, which leads to the use of weak passwords, storing them in insecure locations, and reusing them across different accounts.
This leads to serious data breaches which can affect you and your assets very hard. Cybercriminals are looking for an opportunity sitting at their desk guessing your passwords through your common details and eventually becoming rich by draining your bank accounts.
According to research by the World Economic Forum, 80% of data breaches happen due to weak and stolen passwords.
This guide will help you understand how password managers actually work behind the scenes, from encryption and master passwords to how your data is secured.
Types Of Password Managers
There are three main types of password managers on the market. While they serve the same purpose, there way of storing your data is differs from one another. These include browser, cloud and local password management systems.
Browsers are usually the first-place users encounter when it comes to entering your credentials. Browser-based password managers are free and built-in. Once you enter any new password, it asks for your permission to whether to save this data for later or not. If you save it, it will autofill next time you want to log in.
But the downside of using browser-based password manager is that its specific to browser. For instance, if you are Chrome user and your passwords are managed and saved with it, they are of no use to you when you go to another browser like Firefox etc.
Cloud Vs Offline
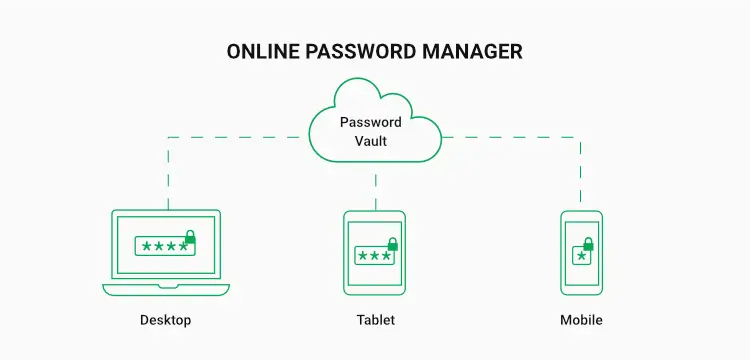
This is where Cloud password managers come in, providing accessibility to be used anywhere you want. However, they are based on some third-party owners whom you are trusting with some of your most sensitive data, even though cloud password managers offer MFA support, automated vault backup and dark web monitoring.
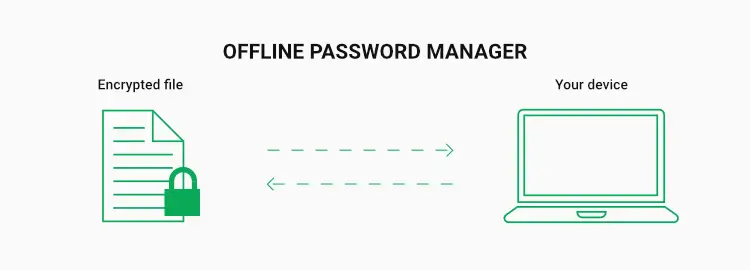
Local password managers like your own local device saving your passwords offers much more security and satisfaction from any attack from outside on your data. However, there is a serious risk of device failure which you used for storing data, therefore, a backup is necessary for using local storage for password management.
Password Managers Encryption And Security
Thanks to the advancement in technology that we today have encryption techniques which offer great comfort when it comes to securing your personal and most important data.
All password managers rely on some sort of encryption to secure user data. Each encryption process (for example, 256-bit AES, RSA or DES) takes a different approach and uses different algorithms to achieve the same goal, using math to encrypt and decrypt information.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
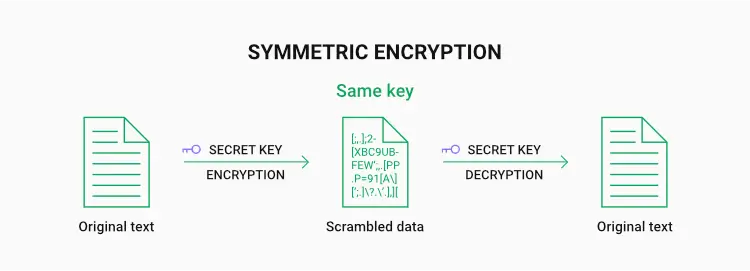
It’s a symmetric type of encryption using the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. It also uses substitution permutation network algorithm to apply many rounds of encryption which is why it requires a huge effort to even try to break the wall.
AES is very efficient in saving and performing operation compared to other encryption methods like DES, which makes it a true winner. It also provides an extra layer of security by using other protocols like SSL and WPA2.
Just imagine what time it would take to crack a 256-bit AES key, which boasts a staggering number of 984,665,640,564,039,457,584,007,913,129,639,936 combinations. Keeping this in mind, we can rely on this technology.
This encryption is used in VPNs, Wi-Fi networks, mobile applications, programming, OS systems, and even in military grade encryption.
DES, AES, and RSA all encrypt data, but with different algorithms. AES as you know by now is very commonly used in password managers due to its wide key length as compared to DES which has gone outdated due to short key length, making it vulnerable to breach.
RSA, in contrast, uses two keys (public and private), which makes it slower but ideal for securely sharing secrets in the first place.
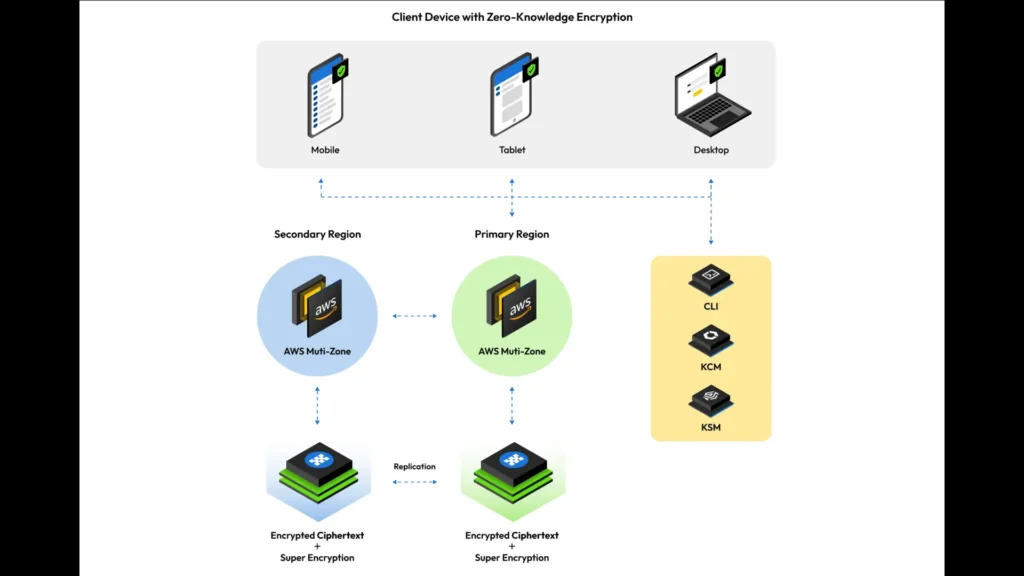
One of the main reasons for relying on password managers is their zero-knowledge architecture, similar to WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption model. This means that even your password manager provider is not able to see what’s in your vault and how much valuable it is. When you enter a master password or enter your vault, it is encrypted on your device before being sent to the password manager’s server.
Risks Involved With Using Password Managers
Even though there are very low chances of facing any security issues if you apply password management best practices, there are still certain risks to consider when and before using the password management systems.
Reliability comes first in the discussion when it comes to risks involved in saving passwords to managers. Less reliable password managers can cause serious trouble for you as they are more prone to cyber-attacks. Other than that, some password managers might lack proper security protocols, like those which offer free versions along with paid ones as well. I think these are among the most serious dangers users face.
Second major point is the relief of having backup to your saved data with servers. While there is no guarantee to server breakdown, if they do, your only hope left is that it has a backup copy as well. As discussed before this risk increases multi-fold if you are storing your passwords locally.

Naturally, keeping your own backup on an unprotected disk drive or poorly protected cloud service won’t help either. Fortunately, there are providers like NordPass and 1Password that keeps backup of main server data in case a server breakdown happens.
You may be able to sync your password manager account across all your devices including mobile phone, tablet, desktop computer, laptop or a watch. But if one of your devices becomes vulnerable to risk of facing malware, you are gone.
To be in a secure position, I would recommend you use any reliable antivirus software in your systems to avoid intrusion and storing of any malware data in your systems.
Myths Surrounding Password Managers
The myths surrounding password managers stem from a lack of understanding and fear of technology. Many think that password managers despite their hype are insecure to use and rely on. However, it is not true in case you do a little research and choose one which is more secure and provides advanced features that help in multi-layer protection.
It is not practical to think of these managers as a highly complex and difficult to use software. They provide very user-friendly, intuitive interfaces that make it convenient to use them, store data, and retrieve it. Even, some password managers are likely to integrate with your browsers and devices allowing easy and one-click logins.
Another myth is that a reliable and secure manager is not affordable for many. While many password managers offer free to use basic versions along with paid versions, there are also those which offer premium security with affordable pricing. Considering their investment in security and usage of protocols to build extra security, it is worth to cost a little higher for them.
If you fear that your passwords might leak in case of data breach at server end, it is not true at all. Secure and reliable password managers have end-to-end encryption to protect your data, so even if their servers are compromised, no one will be able to decipher your codes.
Why They Matter?
Choosing a trustworthy password manager that employs reliable encryption can make you enjoy enhanced protection to all your stored items, including your devices, passwords, payment card numbers, pins, social security numbers, birth dates, identification data, or door codes.
As long as you create a strong master password and incorporate Two-Factor Authentication or MFA, you can be sure that no one will be able to access your vault and confidential information. And you certainly cannot achieve that level of security with post-it-notes, note apps, or spreadsheet documents.
Using password managers also helps build safe data protection habits along with privacy protection education. You no longer need to use and store your secret data in a file on desktop or in multiple folder layers to satisfy yourself hypothetically.

Not only that, password managers also bring convenience into your life. You don’t need to remember passwords and carry your notebook containing your pins with you in case you need to login into another device.
If you sync your accounts across different devices, you can always access them, no matter where you are. Additionally, when it comes to sharing passwords, many password managers make the process really quick, easy and safe.
Are password managers safe? Absolutely. But they are only as effective as the person using them. If you use a very generic and easy to guess password as the password of all your accounts and turn off MFA, then it doesn’t matter whether you are using some cheap free version of password manager or a premium security one. How secure your vault is, someone is going to guess that password eventually.
More Guides
Android vs iPhone In 2026 – A Practical Buyer’s Guide
SSD vs NVMe vs HDD – Which Storage Type Makes Sense in 2026
WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7 – What’s the Real Difference for Everyday Users?


